Myocardial Infarction: How To Prevent It?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), each year around 12 million people die of myocardial infarction or stroke in the world. It is one of the most common causes of mortality on the entire planet.
Despite being a very frequent and dangerous pathology, 80% of myocardial infarctions are preventable. How can they be avoided, then? Find out in this article.
What is myocardial infarction?
In order for the heart to pump blood and send it to the rest of the body, it needs energy and nutrients. To do this, like other organs, it has a series of blood vessels called coronaries , which are responsible for transporting the necessary blood to the cells of the heart or cardiomyocytes.
When these coronary vessels, for whatever reason, become obstructed, blood does not reach the heart. The cells are left without oxygen or nutrients and this causes their death. Therefore, a myocardial infarction is the death of a part of the heart due to a lack of blood supply.
Why are the coronary vessels blocked?
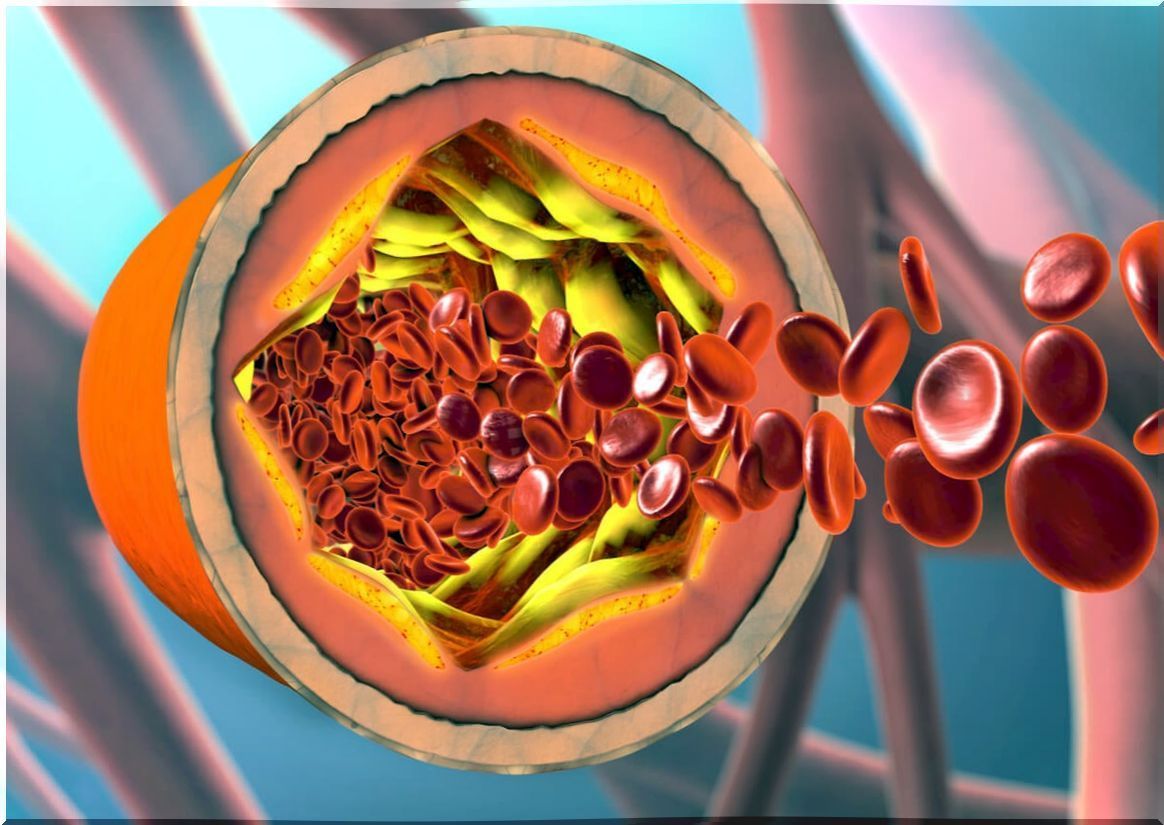
The most common cause of occlusion or obstruction of these vessels is the formation of fatty plugs, which is technically known as atheroma plaques . As we age, the arteries become thicker and less elastic, and can even become calcified. This natural aging process of the arteries is called arteriosclerosis .
In contrast, we have atherosclerosis , which is a pathological process. It is based on the formation of atheroma plaques in large arteries, especially the aorta, coronary, carotid, iliac, and femoral arteries. These plaques of atheroma develop progressively. It begins with the deposit and accumulation of LDL cholesterol ( bad cholesterol ).
But this is not that it happens out of nowhere, but that the wall usually has an injury before, caused by genetic and environmental factors. The pathological plaque sits on this lesion. LDL causes arterial walls to swell and attract macrophages, the body’s defense cells.
To try to stop the inflammation and what is doing damage to the arteries, the macrophages will ingest the bad cholesterol. However, instead of fixing the problem, they will turn into foam cells, that is, cells full of fat that, when they die, leave LDL free.
The foam cells will release signals that will promote the transformation of the arterial smooth muscle cells so that they manufacture a collagen shell around this fat core, making it larger and larger. When blood passes through the damaged wall, it deposits fibrin and platelets to fix it. However, they further promote the growth of atheroma plaque.
What are the risk factors for myocardial infarction?
Different studies reveal that there are certain factors that increase the probability of having a heart attack. In other words, they are risk factors. The three most relevant are the following:
- Tobacco use: tobacco smoke contains different substances that are harmful to the lungs, but also to the blood vessels and the heart.
- The unhealthy diet: When a person consumes a lot of trans fats, sugars and salt, they increase their risk of suffering diseases such as hypertension and diabetes, which damage the coronary vessels.
- Physical inactivity : sedentary lifestyle is behind the lack of adequate blood circulation, strongly associated with cardiovascular risk.
On the other hand, there are also diseases that promote the risk of having a heart attack. If you have more than one of these conditions at the same time, your arteries are more likely to be damaged. Here we can mention high blood pressure, hypercholesterolemia and diabetes.
Arterial hypertension
Blood pressure is the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the vessels. At higher tension, the arterial walls will suffer more damage, stimulating the deposit of LDL cholesterol.
Normal blood pressure values are those that do not exceed 120 millimeters of mercury in systole, nor 80 millimeters of mercury in diastole. The variation is closely linked to lifestyle and diet. Increases in salt intake or sedentary lifestyle, lead to increases that can become chronic.
High blood sugar or diabetes
In a 2008 study, it was observed that people with diabetes developed atherosclerosis more rapidly than non-diabetics. This is explained because high blood glucose activates factors that promote macrophage mobilization. In addition, it increases the oxidation and inflammation of the arterial walls.
On the other hand, diabetes is not only the increase in blood sugar, but also increases insulin resistance, the accumulation of lipids and the loss of the regulatory function of arterial cells. Thus, an inflammatory environment is created.
High lipid level or hypercholesterolemia
The bad lipids are LDL, transported by the blood through proteins. The target of the LDL protein is the tissues and the various organs for its utilization. When there is an excess of them, they stay in the arteries.
Lowering cholesterol is a difficult task for some people. Factors are involved that are not only related to diet, but also to physical activity, genetics and liver metabolism. Current eating styles do not favor a lowering of lipids, as fast and fat-saturated food is the most common.
Tips to prevent myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is not an affectation that occurs randomly, but it has a lot to do with our way of life. Therefore, we will give you a series of tips to prevent it, which are the following:
- If you smoke or use tobacco in any other way, it is best to quit. If you can’t on your own, you have different aids at your disposal. You can contact your family doctor for advice on smoking cessation drugs.
- You have to dedicate at least 30 minutes a day to physical activity, especially aerobic exercises such as swimming, walking, cycling and even doing housework.
- The diet must be balanced. In addition, the consumption of salt, fat and sugar should be reduced.
- An important aspect of preventing heart attacks is counseling people at high risk of suffering them. That is, if you have a high weight, hypertension, diabetes or high blood lipids, you should go to your family doctor to offer you the best possible treatment.