Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Everything You Need To Know
Science still knows little about Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Despite this, today this disease has a much better prognosis than in the past, thanks to the development of new treatments.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a rare disease. It is estimated that it affects between 1 and 2 people per million inhabitants, being more common in women. It is usually diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50, but can appear at any time in life.
The main characteristic is that there is excessive secretion of acid in the stomach. This leads to ulcers forming there. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is considered a serious disorder and is often resistant to treatment.
What is Zollinger-Ellison syndrome?
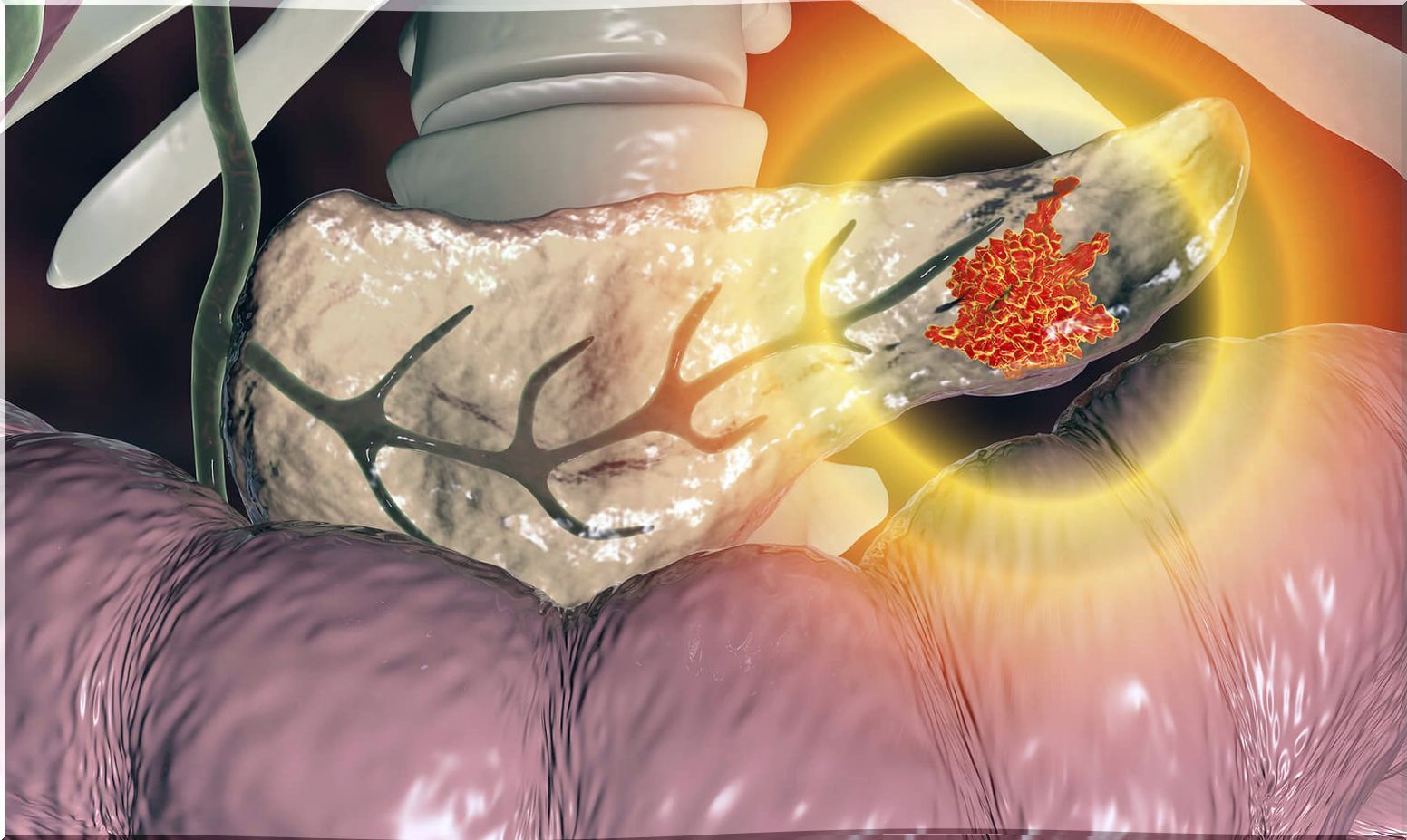
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is a condition in which one or more tumors form in the pancreas or duodenum, which is the upper part of the small intestine. These tumors are called gastrinomas .
Gastrinomas secrete a hormone called gastrin in large amounts. This leads to the stomach producing more acid than normal. The direct effect is the continuous production of peptic ulcers.
The tumors are small and slowly growing. In about 50% of cases these formations are malignant. Likewise, half of the patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome have multiple tumors.
Between 10 and 20% of those affected develop tumors in other parts of the body: stomach, splenic hilum, mesentery, lymph nodes or ovaries. About 40 to 60% of those with this condition also have a condition called multiple endocrine neoplasia .
What are your causes?
Science does not know the precise reason why Zollinger-Ellison syndrome occurs. What is known is that it begins with one or more tumors that secrete large amounts of gastrin. If they are malignant they can spread throughout the rest of the body.
Scientists have found a link between Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1). This is a hereditary disease in which there is hyperactivity in the endocrine glands. This causes the characteristic tumors to form.
MEN 1 results from a defective gene that is associated with a protein called menin . A person who has blood relatives with this disease is more likely to develop Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome can cause symptoms such as the following:
- Pain in the abdomen: discomfort, burning sensation or excruciating pain
- Diarrhea.
- Heartburn and reflux.
- Reduced appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Involuntary weight loss
- Bleeding from the digestive tract
The symptoms of this condition are very similar to those of a peptic ulcer, but they are more persistent, but just as intense. Many times it is treated as if it were an ulcer disease, with drugs designed for it.
The problem is that some medications may mask the symptoms and make the diagnosis more confusing. Therefore, the doctor should be informed if omeprazole, cimetidine or famotidine has been ingested for long periods.
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is made based on clinical symptoms, medical history and through some tests such as the following:
- Blood test: the goal is to evaluate gastrin levels. A high level is not conclusive, since in other pathologies it is also elevated.
- Gastrointestinal endoscopy: an instrument equipped with a light and camera is inserted to explore the digestive tract, looking for ulcers. It also allows a tissue sample or biopsy to be taken to detect gastrin-producing tumors.
- Endoscopic ultrasound: the endoscope carries a probe and makes it easier to detect tumors. It also allows a tissue sample to be taken.
- Others: Other tests may also be ordered, such as somatostatin receptor scintigraphy, ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
Therapeutic approach
Treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is aimed at both tumors and ulcers. It is not common to go to surgery to remove the neoplasms, since they are usually very small and are located in different parts.
Typically, tumors are treated by procedures such as embolization or radiofrequency ablation. Chemotherapy is also used to slow growth and drugs to relieve symptoms.
The first-line treatment to address excessive acid production is drugs known as proton pump inhibitors . These block the secretion of acid in the cells. Sometimes a drug similar to the hormone somatostatin is also used to counteract the effects of gastrin.

Possible complications of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
The most serious complication is the tumor spreading to other organs. It usually travels from the pancreas or duodenum to nearby lymph nodes or the liver.
Another serious complication is perforation or bleeding caused by ulcers in the stomach and duodenum. Also, severe diarrhea and severe weight loss may occur.
Forecast
The cure rate is low, even when the tumor is found early and can be removed. Despite this, they grow slowly, so people live many years after being diagnosed.
The prognosis is less promising in the case of malignant tumors. If there is metastasis to the liver, only between 20 and 40% of those affected survive more than 10 years. People with MEN 1 have a high survival rate and only in 15% of cases does the disease have an aggressive course.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is the sign of something wrong
The prognosis for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome has improved significantly in the last 25 years. In the past, the leading cause of death was gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, caused by ulcers.
Today drug treatment has significantly reduced mortality from these causes. Unlike other diseases, the most serious complication is metastasis to the liver and not to the lymph nodes. Therefore, its detection implies a risk that should not be overlooked.