Essential Tremor: Symptoms, Causes And Treatments
Essential tremor is common in the general population. Within movement disorders it is the most common pathology, widely surpassing Parkinson’s disease. Statistically, it is twenty times more prevalent than Parkinson’s in adults.
The age group most affected are people over 65 years of age. But between the ages of 40 and 60 is considered the most common age when symptoms first appear. Cases have also been recorded in infants.
The characteristic of essential tremor is involuntary movement in the form of persistent jerks. The manifestation occurs mainly in the upper limbs: hands and arms. The episodes usually appear symmetrically and with pauses.
Although it is a chronic situation, which lasts over time, it is not present throughout the day and sometimes not even every day. Essential tremor is not fatal, it is not associated with cognitive impairment or degeneration of the nervous system.
However, although it is classified as benign, it is a very important disorder for those who suffer from it. It can be said that it represents a cause of disability for activities of daily life, such as writing, having a cup of tea or tying shoes.
Causes of essential tremor
There are not enough studies in the scientific world to reach the cause of the origin of the pathology. This is because it is a benign disorder, with a slow evolution.
However, it is known that essential tremor refers to an alteration in the connections of the nervous system in the nuclei of movement. The thalamus, the nigrostriatal pathway, and the cerebellum are regions of the nervous system responsible for regulating body movements.
The scientific hypothesis is that, in essential tremor, some of these regions has an abnormal change that finally produces involuntary movement.
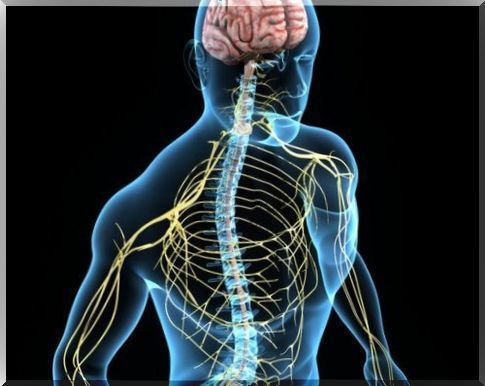
The existence of family cases, in which parents and children suffer from essential tremor, first confirms a genetic component of the alteration. In fact, an equivalent name for essential tremor is ‘familiar tremor’.
Symptoms of essential tremor
First, we must differentiate it from Parkinson’s. The key fact is that in essential tremor, involuntary movements occur when the person performs a specific movement or tries to maintain a posture. In Parkinson’s, the involuntary movements are at rest.
In addition to the key sign, which is tremor in the upper limbs, the following symptoms may appear:
- Voice changes: Essential tremor can affect the larynx, altering the generation of voice in the vocal cords.
- Nodding: as if the person were saying ‘yes’ or ‘no’ with the head, but involuntarily.
- Problems to carry out activities of daily living: sometimes, the tremor is not sufficiently evident, but the person finds that it is difficult for him to grasp something, handle a tool or simply write.
If left untreated, symptoms tend to worsen with age and aging. They have been shown to get worse and more repetitive when a person consumes a lot of caffeine. Also in stressful situations or before a bad night’s rest.

Treatment options
We must clarify that there is no curative treatment for essential tremor. The hygienic-dietetic measure that is always indicated is to suspend caffeine consumption. Various courses of action are recommended for stress, such as psychotherapy or medication to fall asleep.
Some patients benefit from kinesiotherapy and physical therapy sessions aimed at improving muscle control and increasing balance coordination.
Regarding the use of pharmacological treatment, we can mention the following drugs as the most used and the ones with the most evidence in their favor:
- Propanolol: it is a beta blocker. Possibly the most effective in reducing symptoms. It should be used with care in patients with cardiac pathologies, especially if there is a history of blockages, and always supervised by a professional.
- Primidone: is an anticonvulsant.
- Antidepressants: in order to control the stress that may underlie.
- Anxiolytics: to control stress and to regulate sleep.
- Botulinum toxin: it is used in injectable doses in certain areas of the body, mainly the head and hands.
If all of the above does not work, more complex treatments are currently used. These are reserved for patients with a very low response to drugs and a disabling clinical picture. We can name the following therapeutic options:
- Stereotactic radiosurgery: is the use of high-power radiofrequency rays focused on a specific area of the nervous system.
- HIFU: it is the same foundation as the previous technique, but in this case with ultrasound rays.
- Stimulator implant: A device is placed that will send electrical stimuli to the thalamus.
- Thalamotomy: is the excision of parts of the thalamus by surgery. Today, the traditional technique is supplanted by the use of radiosurgery or HIFU, which avoids surgical invasion.